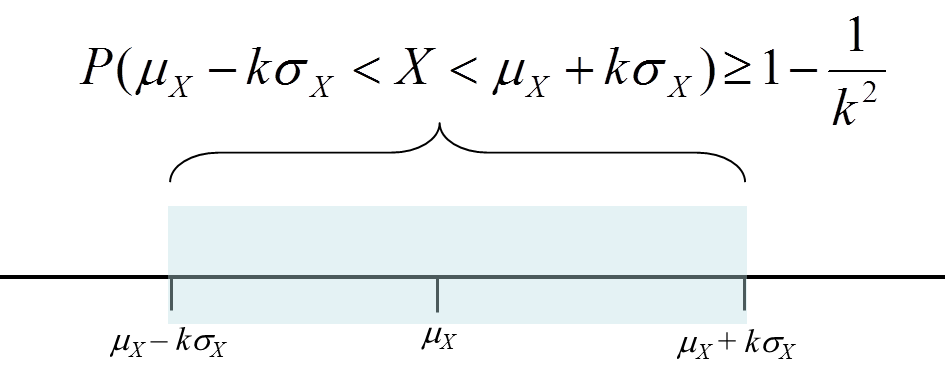This lesson is free - just sign in to access it.
This lesson is a part of the course Statistical Concepts and Market Returns
Ask questions about this lesson and get instant answers.
Chebyshev’s Inequality is used to describe the percentage of values in a distribution within an interval centered at the mean.
It states that for a distribution, the percentage of observations that lie within k standard deviations is atleast 1 – 1/k2
This is illustrated below: