Common Size Income Statement
Test Your Knowledge
Check your understanding of this lesson with a short quiz.
Check your understanding of this lesson with a short quiz.
Ask questions about this lesson and get instant answers.
In a common size income statement each item is expressed as a percentage of revenue. A common-size statement helps in comparison of different companies as it eliminate the effects of size of the business. Common size income statement can be used to time-series analysis of the same company over time or to perform cross-sectional analysis across firms.
Presented below are the standard income statements and common size income statements of two companies ABC and XYZ for the year 2013.
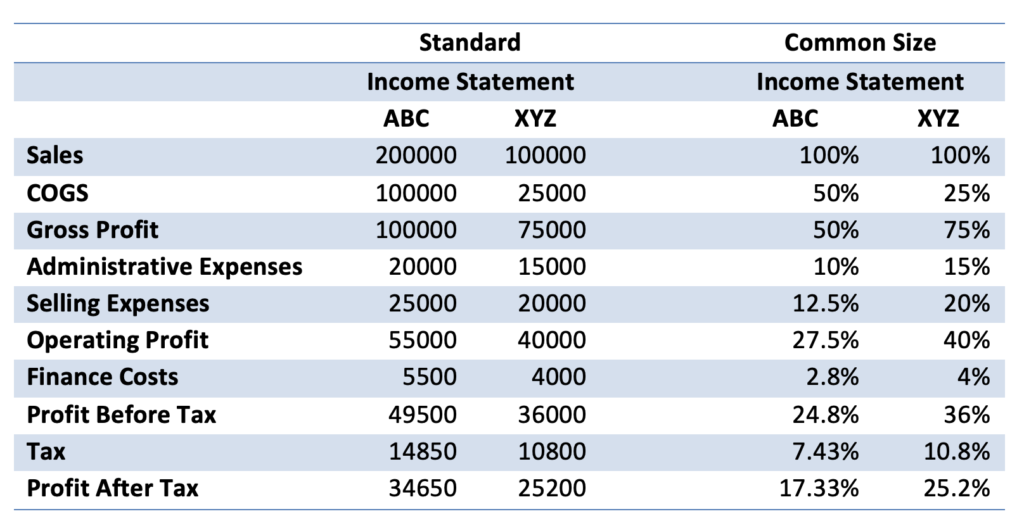
Note that when you see the income statements in terms of absolute dollars, the Company ABC is bigger and more profitable than company XYZ. However, common size statements reveal that company XYZ has a higher net profit compared to company ABC.