Industry Analysis
This article will describe elements of industry analysis beyond Porter’s Five Competitive Forces.
Sample Steps for an Industry Analysis
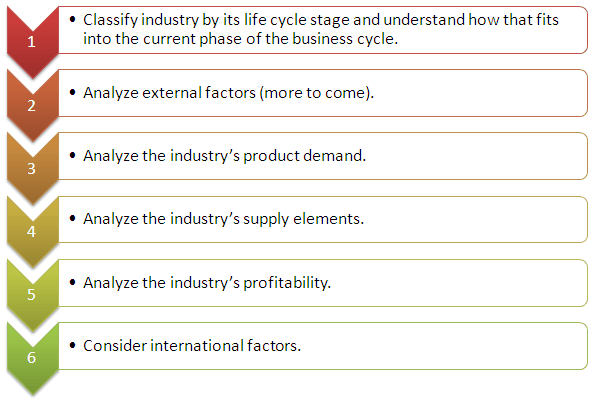
Industry Life Cycle
Industries tend to follow a natural progression which can be outlined as follows:

1) Pioneer Stage: a high degree of uncertainty at this point. The product is unproven and cash flow is most likely negative, but future growth prospects are high. Investors face a high risk/high reward situation with companies in the Pioneer Stage.
2) Growth Stage: now sales and profits are increasing. The product is gaining acceptance, but total market size potential is still not fully known. Star equity analysts discover growth industries ahead of the herd.
3) Mature Stage: the industry has become saturated and growth rate will slow to the rate of general economic growth. Growth companies can still be found within mature industries, as they may be improving the product’s quality or acquiring competitors.
4) Decline Stage: demand for the industry’s product is contracting and the surviving firms fight for market share. Profit margins will shrink and some firms will fail or leave the industry. Stronger firms may anticipate product decline and diversify their operations.
Industry Classifications and Business Cycle Reactions
While industries can be classified by their lifecycle phase, they must also be considered within the context of how they react to the business cycle.
The table below describes industries by business cycle:
| INDUSTRY TYPE | BUSINESS CYCLE TRAITS | LIFECYCLE TRAITS |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Industry |
Test Your Knowledge
Check your understanding of this lesson with a short quiz.
