Lesson 13 of 17
Economic Growth and Inflation
Test Your Knowledge
Check your understanding of this lesson with a short quiz.
Check your understanding of this lesson with a short quiz.
Ask questions about this lesson and get instant answers.
We can explain economic growth and inflation using the Aggregate Demand and Long Run Aggregate Supply curves.
Economic growth is the persistent growth in potential GDP, while inflation is the persistent increase in general prices as shown in the graph below:
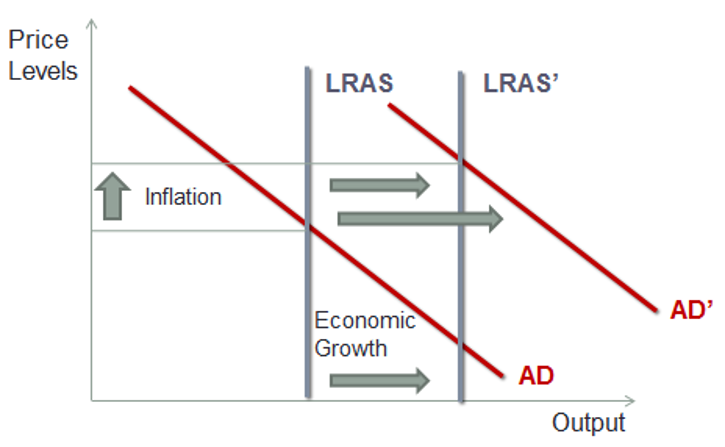
As you can see both AD and LRAS have shifted to the right. Increase in LRAS brings economic growth. This happens due to increased labour, more capital, or better technology. However, there is a bigger increase in Aggregate Demand (AD), which causes inflation.