Lesson 7 of 14
Ask questions about this lesson and get instant answers.
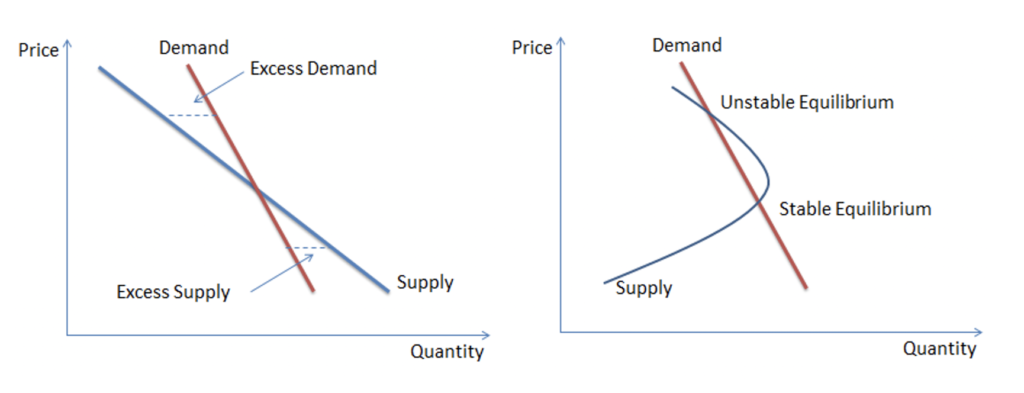
When the demand and quantity deviate from their equilibrium levels, the market forces will interact with each other to bring the price and quantity back to its equilibrium level. As long as this is possible the equilibrium is labelled as stable.
The equilibrium will be stable as long as the supply curve cuts through the demand curve from above, irrespective of whether the supply curve slopes upwards or downwards. The equilibrium will be stable in both the situations below:

However, there are some situations where the equilibrium is unstable. For example, when the slope of the supply curve is less than the demand curve or when the supply function is non-linear.