Ask questions about this lesson and get instant answers.
In this article, we will learn how to perform correlation analysis on financial data using R programming. R is an excellent programming language for performing data analysis. It can handle a variety of financial data, you can create visualizations, and the analysis that you do in R is reproducible which is important for financial analysis.
We will take randomly generated sample data for two fictitious companies and use that to demonstrate how to conduct a correlation analysis in R.
Ensure that you have R and RStudio installed on your system.
For this tutorial, we will use a package named ‘corrplot’ to visualize the correlation that we will calculate.
1 # Installing the packages
2 install.packages("corrplot")
3 # Loading the packages
4 library(corrplot)
5We'll create some random financial data for two fictitious companies, "FinCorp" and "MoneyCorp".
To do so, we will use the rnorm function in R. The rnorm function in R is used to generate random numbers that follow a normal distribution, which is also known as a bell curve or a Gaussian distribution. In simple terms, rnorm(100, mean=0, sd=1) will generate 100 random numbers that are spread around 0 (the mean), with most of the numbers falling within the range of -1 to 1 (one standard deviation).
1 # Set the seed to make the random numbers predictable
2 set.seed(123)
3
4 # Generate random financial data for FinCorp
5 FinCorp <- rnorm(
Once we have the data for the two companies, we combine it into a single dataset using data.frame() function.
Now that we have the data, we can perform correlation analysis. To calculate correlation between two companies we will use the cor function. This will give us the correlation matrix.
1 # Calculate correlation
2 correlationMatrix <- cor(data)
3
4 # Print the correlation matrix
5 print(correlationMatrix)
6
FinCorp MoneyCorp
We can visualize the correlation using the 'corrplot' package.
1 # Plotting correlation matrix
2 corrplot(correlationMatrix, method = "circle")
3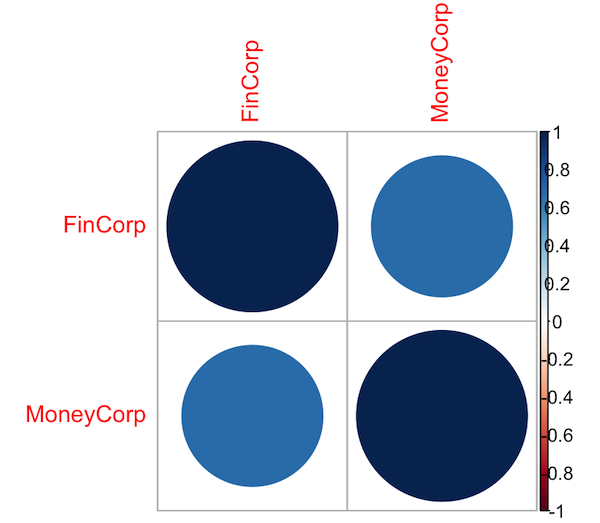
The correlation coefficient ranges between -1 and 1. A result close to 1 indicates a very strong positive correlation between the two variables. A result close to -1 indicates a very strong negative correlation between the two variables. In our example, the correlation between the two companies is 0.6805408, which is positive.
In conclusion, correlation can provide important insights into the relationship between different financial variables. This can be important for diversifying a portfolio and reducing risk.