How to Calculate Yield to Maturity
Yield to Maturity (YTM) is the most commonly used and comprehensive measure of risk. In fact, if someone talks about just ‘Yield’ they are most likely referring to Yield to Maturity.
In simple terms, YTM is the discount rate that makes the present value of the future bond payments (coupons and par) equal to the market price of the bond plus any accrued interest.
Consider the following equation:
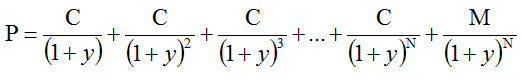
Where:
- P is the bond price
- C is the periodic coupon payment
- N is the number of years to maturity
- M is the (face value) payment at maturity
- y is the “risk-adjusted discount rate” (or yield to maturity, or IRR)
In the above equation, we solve for y, which is the yield to maturity of the bond.
It’s a trial and error process, and you need a spread sheet or a calculator to calculate YTM.
Let’s take a simple example to understand how YTM is calculated. Consider a $1,000 par bond, with 8% coupon and 7 years to maturity. The price of the bond is $1,112.96. Assume that the bond pays coupon semi-annually.
C = $40
N = 2 x 7 = 14
M (face value) = $1,000
P = $1,112.96
Plugging all these numbers in the above equation, we calculate y = 3.00%
In excel you can use Goal Seek to get the YTM. You can also use a calculator such as Texas Instrument BA II to calculate YTM.
Since this bond paid semi-annual coupon, the y we calculated is the semi-annual YTM. We use the bond-equivalent yield convention to calculate the annual YTM. So, YTM = 3.00x 2 = 6%
On the other hand, the effective annual yield is (1.03)2 – 1 = 6.09%
Again, note that YTM is a bond equivalent yield (BEY) which is calculated by applying simple interest rules. So, we annualize the rate by multiplying, instead of using raise to the power. For semi-annual yield, we double the semi-annual yield. For quarterly yield, we will quadruple the quarterly yield.
YTM is a preferred yield measure over current yield because it considers both interest income and capital gains for calculating the returns from the bond. It also includes the reinvestment income.


