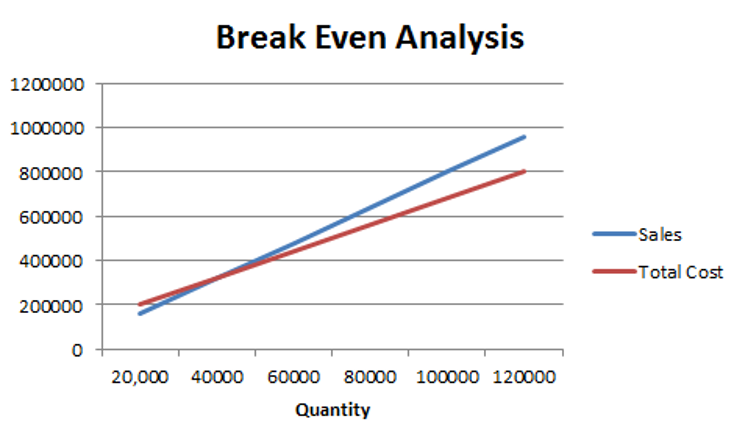
Breakeven Analysis
For a firm, the breakeven point is the quantity of the sales required by the firm to cover its total cost, i.e., Total revenue = Total cost. At this quantity of sales the firm's net income is zero.
We know that:
F includes both fixed operating cost and fixed financing cost.
Breakeven quantity is the quantity where EBIT = 0. So, we solve for Q where EBIT = 0.
Test Your Knowledge
Check your understanding of this lesson with a short quiz.